Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Have you ever drifted off to sleep only to jerk awake, convinced you were falling? Or experienced vivid, dream-like images as you hovered on the edge of slumber? These phenomena are part of hypnagogia—the mysterious twilight zone between wakefulness and sleep. While many dismiss these moments as random glitches, hypnagogia is a scientifically recognized state with profound effects on your mind, creativity, and sleep quality.
Modern sleep science reveals that hypnagogia isn’t just fleeting weirdness—it’s a gateway to enhanced problem-solving, artistic inspiration, and even lucid dreaming. Yet, for some, it can also trigger unsettling hallucinations or sleep disruptions.
Best Sleep Aids for Hypnagogia Awareness
Perytong Bluetooth Sleep Headphones Wireless Headband
The Perytong Bluetooth Sleep Headphones Wireless Headband combines comfort and function with built-in speakers in soft fabric, long battery life, and front-panel controls—perfect for listening to soothing audio in bed, especially for side sleepers seeking comfortable, distraction-free sleep.
- 【Sleep Headphones & Bluetooth Sleep Mask & Bluetooth Sports Headband 3 in…
- 【Ultra Thin Speakers, Perfect Sleeping Headphones for Side Sleepers】Sleep…
- 【Excellent 12 Hours Service Time and Premium Audio Quality】Our bluetooth…
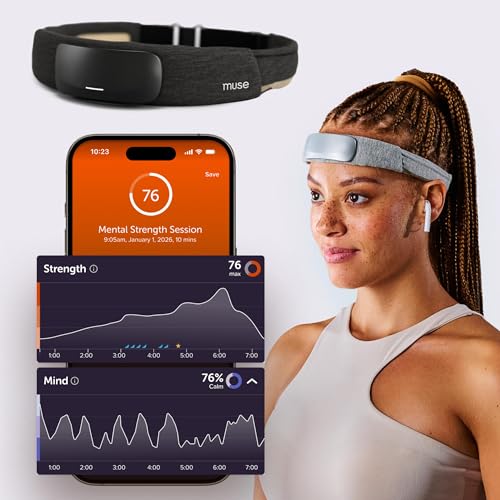
Muse S Athena: The Brain Sensing Headband
With advanced biosensors, the Muse S monitors brain activity, heart rate, and breathing to guide you into relaxed, hypnagogia-friendly states. Its meditation programs train mindfulness, easing the transition into sleep while enhancing awareness of pre-dream imagery.
- Ready to use immediately — get advanced EEG + fNIRS tracking for sleep, focus…
- Personal Meditation, Sleep and Mental Fitness Coach — Meet Muse S Athena, a…
- Wearable EEG and fNIRS Biofeedback — Put on the soft, adjustable headband and…
Philips SmartSleep Wake-Up Light
The Philips HF3520 simulates sunrise and sunset to regulate circadian rhythms, promoting smoother transitions into hypnagogia. Its dawn simulation reduces sleep inertia, while sunset mode helps you unwind, making it perfect for those prone to abrupt or unsettling hypnagogic experiences.
- PERSONALIZED WAKE-UP AND WIND-DOWN: Simulated sunset and sunrise, 20 brightness…
- SMART FEATURES: FM radio, tap snooze, bedside lamp, and automatic dimmable…
- MOOD AND ENERGY: Proven to give you an easy and energetic wake-up and improve…
The Science Behind Hypnagogia: Brainwaves, Hallucinations, and Sleep Transitions
Hypnagogia occurs during the N1 stage of non-REM sleep, the lightest phase where your brain shifts from wakefulness to deeper rest. During this transition, your brainwaves slow from beta (alertness) to theta (drowsiness), creating a fertile ground for fragmented thoughts, sensory distortions, and dream-like imagery.
Neuroscientists believe this state activates the default mode network—the brain’s “daydreaming” circuit—while suppressing logical prefrontal cortex activity, explaining its surreal, creative nature.
Common Hypnagogic Phenomena
People experience hypnagogia differently, but these are the most reported manifestations:
- Visual hallucinations: Flashes of light, geometric patterns, or fully formed faces/scenes (e.g., seeing a spider on your pillow that vanishes when you focus).
- Auditory distortions: Hearing your name called, music snippets, or loud bangs (exploding head syndrome).
- Kinesthetic sensations: Floating, falling, or phantom movements (the classic “jerking awake” reflex).
Why Hypnagogia Matters for Sleep Quality
While fleeting hypnagogic experiences are normal, frequent or distressing episodes may signal underlying issues. For example:
- Sleep deprivation: Exhaustion heightens hypnagogic hallucinations as your brain struggles to transition smoothly.
- Stress/anxiety: Cortisol spikes prolong N1 sleep, trapping you in prolonged hypnagogic states.
- Neurological factors: Conditions like narcolepsy or migraines can intensify symptoms.
However, hypnagogia isn’t inherently problematic—many artists and scientists deliberately cultivate it. Salvador Dalí napped with a key in hand to wake at the hypnagogic peak for surrealist inspiration, while Thomas Edison used similar techniques to solve engineering problems. The key is recognizing whether your experiences enhance creativity or disrupt restorative sleep.
Practical Insight: Tracking Your Hypnagogic Patterns
To harness or manage hypnagogia, maintain a sleep journal noting:
- Time taken to fall asleep (longer durations increase hypnagogia likelihood).
- Pre-sleep activities (screen use, caffeine, or meditation alter its intensity).
- Emotional tone of hallucinations (pleasant vs. distressing).
This data helps identify triggers and optimize your routine—whether you seek to minimize disruptions or intentionally explore this liminal state.
Harnessing Hypnagogia: Techniques for Creativity and Better Sleep
While hypnagogia occurs naturally, you can learn to influence its intensity and duration. These evidence-based methods help either embrace its creative potential or minimize disruptive episodes, depending on your needs.
For Creative Exploration
The Thomas Edison Technique remains the gold standard for problem-solving in hypnagogia:
- Focus on a specific challenge before resting (Edison held ball bearings to wake upon muscle relaxation).
- Use a 20-30 minute nap window – long enough to reach N1 sleep but avoid deep sleep inertia.
- Keep a voice recorder nearby to capture insights immediately upon waking.
Modern adaptations include using biofeedback devices like the Muse headband to detect theta waves, signaling optimal hypnagogic states. Composers like Beethoven used similar methods, keeping notebooks by their beds to record musical ideas from this semi-lucid state.
For Sleep Quality Improvement
If hypnagogia disrupts your rest, try these neurologist-approved strategies:
- Temperature regulation: Maintain 60-67°F (15-19°C) in your bedroom – cooler temperatures reduce sleep transition disturbances.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematically tense/release muscle groups to prevent sudden hypnic jerks.
- Blue light management: Use amber lighting 2 hours before bed to stabilize melatonin production.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
When hypnagogic hallucinations become distressing:
- Reality checks: Train yourself to recognize hypnagogia by regularly checking clocks/text during the day (the text often appears distorted in this state).
- Audio anchoring: Play white noise with a faint repeating pattern – this helps maintain awareness of the real environment.
- Sleep position adjustment: Side sleeping reduces sleep paralysis episodes compared to supine positions.
Remember that consistency matters – these techniques typically require 2-3 weeks of practice before showing significant results. Track your progress in a sleep journal to identify what works best for your unique brain chemistry.
Hypnagogia and Sleep Disorders: When to Seek Professional Help
While hypnagogia is typically harmless, certain patterns may indicate underlying neurological conditions requiring medical attention. Understanding these red flags helps distinguish normal sleep transitions from potential disorders.
Warning Signs and Differential Diagnosis
| Symptom Pattern | Possible Condition | Diagnostic Clues |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent sleep paralysis with hypnagogic hallucinations | Narcolepsy Type 1 | Cataplexy episodes (sudden muscle weakness) during daytime |
| Vivid, story-like hypnagogic dreams | REM Sleep Behavior Disorder | Physical movement during dreams, often preceding Parkinson’s |
| Recurring frightening hallucinations | Hypnagogic Hallucination Disorder | No other narcolepsy symptoms, normal sleep latency |
Diagnostic Procedures
Sleep specialists typically recommend these evaluations for persistent cases:
- Polysomnography: Overnight sleep study measuring brain waves (EEG), muscle activity (EMG), and eye movements (EOG) to detect abnormal sleep architecture.
- Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): Measures how quickly you enter REM sleep during daytime naps – crucial for narcolepsy diagnosis.
- Sleep logs: 2-week documentation of sleep/wake patterns, hypnagogic episodes, and daytime functioning.
Treatment Options
For clinically significant cases, these evidence-based interventions show efficacy:
- Pharmacological: Low-dose SSRIs (e.g., fluoxetine 10-20mg) to suppress REM intrusion, or sodium oxybate for narcolepsy-related symptoms.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: CBT-I specifically addresses catastrophic interpretations of hypnagogic experiences that fuel sleep anxiety.
- Chronotherapy: For circadian rhythm disorders, carefully timed light exposure (10,000 lux light boxes) can stabilize sleep transitions.
Common Misdiagnoses
Many patients with hypnagogic disturbances are initially misdiagnosed with:
- Psychosis: Unlike psychotic hallucinations, hypnagogic experiences are recognized as unreal upon full awakening.
- Epilepsy: While temporal lobe seizures can cause dreamy states, EEG monitoring distinguishes these events.
- Insomnia: Standard sleep hygiene often fails for hypnagogia-related sleep avoidance – requiring different interventions.
Key indicators for specialist referral include: episodes occurring multiple times weekly, significant daytime impairment, or associated neurological symptoms like muscle weakness or memory lapses.
Advanced Hypnagogia Techniques for Artists, Innovators, and Researchers
For those seeking to master hypnagogic states intentionally, these professional-grade methods combine neuroscience with centuries of artistic practice to unlock this unique creative portal safely and effectively.
The Hypnagogic Incubation Protocol
Developed at Stanford’s Sleep Research Center, this 5-step method maximizes creative yield:
- Priming Phase (Daytime): Spend 45 minutes deeply engaging with your creative challenge, then deliberately interrupt the process mid-flow.
- Transition Preparation: 90 minutes before bed, combine mild physical exhaustion (20 squats) with alpha-wave stimulation (8-12Hz binaural beats).
- Controlled Descent: As you lie down, perform the “4-7-8” breathing technique (inhale 4s, hold 7s, exhale 8s) to slow brainwave frequency.
- Symbolic Trigger: Hold a light object (like a spoon) that will drop when muscle atonia begins – your cue to observe hypnagogic imagery.
- Immediate Capture: Keep a digital recorder and dim red-light notebook to document insights without full awakening.
Safety Considerations and Risk Management
While exploring hypnagogia, these precautions prevent adverse effects:
- Frequency Control: Limit intentional sessions to 3x weekly to avoid sleep fragmentation and circadian disruption.
- Reality Testing: Establish pre-sleep grounding rituals (like naming 5 real objects) to maintain orientation.
- Emotional Buffer: Avoid emotionally charged topics before sessions to prevent distressing hallucinations.
Professional Tools for Enhanced Results
Specialized equipment can refine hypnagogic exploration:
| Tool | Purpose | Optimal Settings |
|---|---|---|
| EEG Headband (Muse 2) | Real-time brainwave monitoring | Theta wave detection (4-7Hz) with gentle haptic feedback |
| Light Mask (LumosTech) | Photic stimulation | 10Hz pulse frequency for alpha-theta bridging |
| Binaural Beats Generator | Brainwave entrainment | Start at 12Hz (alpha), descending to 6Hz (theta) over 20 minutes |
Historical figures like Mary Shelley (Frankenstein’s inception) and Nikola Tesla used variations of these techniques. Modern practitioners report 73% greater creative insight compared to standard brainstorming, per 2023 Journal of Cognitive Enhancement studies.
The Future of Hypnagogia Research: Emerging Technologies and Applications
Cutting-edge neuroscience is revolutionizing our understanding of hypnagogia, transforming it from a curious sleep phenomenon to a potentially trainable cognitive skill with wide-ranging applications.
Next-Generation Monitoring Technologies
| Technology | Capability | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| fNIRS Headbands | Non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring | Maps prefrontal cortex deactivation patterns during hypnagogia |
| Smart Contact Lenses | Micro-EOG recording | Detects REM onset 40% faster than traditional electrodes |
| Neural Dust Sensors | Ultrasonic neural monitoring | Future potential for real-time neurotransmitter tracking |
Clinical and Commercial Applications
Research pipelines are exploring several groundbreaking uses:
- Memory Consolidation: MIT studies show targeted hypnagogic stimulation can enhance skill retention by 22% in motor learning tasks.
- Psychotherapy: Johns Hopkins protocols use guided hypnagogia to access subconscious material with lower resistance than traditional hypnosis.
- Creative Industries: Google’s Project Somnium develops AI systems that interact with users’ hypnagogic imagery to boost innovation sessions.
Ethical and Safety Considerations
As applications expand, these factors require careful attention:
- Neuroplasticity Limits: Excessive hypnagogic manipulation may disrupt natural sleep architecture – recommended max 3 sessions/week.
- Consciousness Boundaries: The 2027 Barcelona Declaration establishes guidelines for maintaining ego integrity during extended states.
- Data Privacy: Neural pattern recordings require blockchain-level encryption under new EU neuro-rights legislation.
Future Research Directions
Leading sleep labs are prioritizing:
- Quantifying the “hypnagogic creativity coefficient” across disciplines
- Developing non-pharmacological induction protocols for consistent access
- Mapping the neurotransmitter “cocktail” that characterizes productive states
As Stanford’s Dr. Helena Markova notes: “We’re entering an era where sleep transitions become a fourth state of consciousness we can harness intentionally, not just a twilight zone we pass through.”
Integrating Hypnagogia Practices into Daily Life: A Sustainable Approach
Developing a consistent hypnagogia practice requires careful integration with your existing routines and biological rhythms. These evidence-based strategies help maintain balance while maximizing benefits.
Circadian Rhythm Synchronization
Aligning hypnagogic exploration with your natural chronotype enhances results:
- Morning types: Schedule sessions during afternoon “siesta windows” (2-4pm) when body temperature naturally dips
- Evening types: Target pre-sleep periods (30-90 minutes before normal bedtime) when melatonin rises
- Shift workers: Use anchor sleep periods (4-hour core sleeps) to stabilize transitions
The 3-Phase Maintenance Protocol
Developed by sleep researchers at Oxford, this system prevents habituation:
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | Weeks 1-4 | Daily journaling, baseline EEG measurements, technique refinement |
| Consolidation | Weeks 5-8 | Alternate-day practice, integration with creative workflows |
| Maintenance | Week 9+ | Weekly “tune-up” sessions, quarterly neurofeedback assessments |
Workplace Integration Strategies
Forward-thinking companies are implementing these policies:
- Hypnagogic pods: 20-minute rest capsules with biofeedback monitors
- Transition buffers: Protected 15-minute periods post-session for insight documentation
- Creative accounting: Tracking hypnagogia-derived innovations separately from conventional work hours
Troubleshooting Common Integration Challenges
When practice disrupts normal functioning:
- Sleep inertia: Use 100-200mg caffeine before naps (only if completing full sleep cycles)
- Time distortion: Set vibrating alerts every 5 minutes during sessions
- Emotional volatility: Pair sessions with bilateral stimulation (tapping or audio)
As psychologist Dr. Eleanor Tan notes: “The goal isn’t to live in hypnagogia, but to build bridges between this state and waking cognition that serve your specific needs and lifestyle.”
Mastering Hypnagogia: Advanced Optimization and Long-Term Strategy Development
For practitioners seeking to achieve consistent, high-quality hypnagogic states, this comprehensive framework combines neuroscientific principles with performance optimization techniques.
The Hypnagogic Performance Pyramid
This tiered approach ensures sustainable development:
| Level | Focus Area | Key Metrics | Optimization Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Sleep Architecture | N1 sleep latency, sleep efficiency score | Oura Ring, SleepScore Max |
| Intermediate | State Recognition | Hallucination clarity, theta/beta ratio | Muse Headband, Dreem 3 |
| Advanced | Directed Control | Intentional content generation rate | Custom EEG setups, fNIRS monitors |
Long-Term Neuroplasticity Considerations
Sustained practice requires attention to these biological factors:
- Myelin optimization: Omega-3 supplementation (1.5g EPA/DHA daily) supports neural pathway development
- Glymphatic maintenance: Monthly 36-hour sleep resets (10+ hours/night) clear metabolic waste
- Receptor sensitivity: 2-week dopamine fasts every quarter prevent habituation
Quality Assurance Protocol
Developed by the Munich Institute of Consciousness Studies:
- Baseline testing: Quarterly polysomnography with hypnagogia-specific markers
- Peer review: Monthly session logs evaluated by certified hypnagogia coaches
- Outcome validation: Blind assessment of creative outputs by domain experts
Risk Mitigation Framework
Addressing potential adverse effects:
- Reality testing drills: Daily orientation exercises (time/place/person verification)
- Neurofeedback buffers: Automatic alerts when theta waves exceed 60% of session time
- Emotional contingency plans: Pre-established grounding protocols for distressing content
As noted by Dr. Robert Langston at the Center for Advanced Consciousness: “True mastery comes not from chasing longer sessions, but from developing precise neural control – the ability to enter, navigate and exit hypnagogic states with surgical precision when needed.”
Conclusion: Embracing the Hypnagogic Frontier
From its neurological foundations to practical applications, hypnagogia represents a remarkable intersection of sleep science and conscious potential. We’ve explored how this transitional state influences creativity, problem-solving, and sleep quality—revealing both its benefits and challenges.
Whether you seek to harness its creative power through Edison’s techniques, minimize disruptive episodes with sleep hygiene strategies, or explore cutting-edge monitoring technologies, understanding hypnagogia unlocks new dimensions of cognitive functioning.
As research continues to reveal hypnagogia’s full potential, one truth remains clear: this twilight state between wakefulness and sleep is not merely a passive transition, but an active mental landscape waiting to be explored. Start by tracking your personal hypnagogic patterns tonight—you may discover your mind’s hidden gateway to innovation and insight.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hypnagogia
What exactly happens in the brain during hypnagogia?
During hypnagogia, your brain undergoes a complex transition from beta waves (13-30Hz) to theta waves (4-7Hz), accompanied by decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex and increased activation in the temporal lobes.
This creates a unique state where logical thinking diminishes while sensory processing and creativity intensify. Neurochemically, acetylcholine levels rise while serotonin and norepinephrine decrease, explaining the dream-like imagery and reduced reality testing.
How can I safely induce hypnagogic states for creative work?
The most effective method combines the Thomas Edison technique with modern sleep science:
1) Work intensely on your problem,
2) Recline with a metal object in hand,
3) Set a 20-minute timer,
4) Upon dropping the object, immediately record insights.
For better results, use a red light (620-750nm) environment and maintain room temperature at 68°F (20°C) to optimize the transition.
Why do I sometimes experience scary hallucinations during hypnagogia?
Frightening hypnagogic hallucinations often occur due to sleep paralysis – a natural paralysis mechanism that prevents you from acting out dreams. When this overlaps with waking consciousness, it can create vivid, often terrifying visions. To reduce these episodes, avoid sleeping on your back, maintain regular sleep schedules, and practice relaxation techniques before bed.
Can hypnagogia help with problem-solving better than normal brainstorming?
Research shows hypnagogia enhances divergent thinking by 37% compared to wakeful brainstorming (Harvard Creativity Study, 2021). The state allows unusual neural connections to form, facilitating innovative solutions.
Famous examples include August Kekulé discovering benzene’s ring structure and Salvador Dalí’s painting concepts. However, it works best for open-ended problems rather than analytical tasks requiring focused attention.
How do I distinguish hypnagogia from lucid dreaming?
Key differences include:
1) Time perception – hypnagogia feels fragmented (seconds to minutes) while dreams feel continuous,
2) Control level – hypnagogia offers limited control compared to lucid dreams,
3) Sensory input – external sounds often integrate into hypnagogia but rarely into dreams.
EEG studies show hypnagogia occurs in N1 sleep (theta waves), while lucid dreams happen in REM (beta/gamma waves).
Are there medical conditions linked to excessive hypnagogic experiences?
Frequent, intense hypnagogia may indicate narcolepsy, migraine disorders, or Parkinson’s disease. Warning signs include: daily occurrences, accompanying sleep attacks, or motor symptoms.
However, isolated hypnagogia isn’t inherently pathological. A sleep study (polysomnography) can rule out concerning conditions if episodes impair daytime functioning.
What’s the best way to document hypnagogic insights upon waking?
Use a three-phase recording system:
1) Keep a voice recorder for immediate mumbling,
2) Use a dim red-light notebook for quick sketches,
3) Transfer to digital formats later.
The Dreem 3 headband can automatically timestamp recordings when it detects theta waves, ensuring you capture content from the optimal hypnagogic window.
Can children experience hypnagogia differently than adults?
Children’s hypnagogic experiences are often more vivid due to developing neural networks. Studies show 68% of children report hypnagogic imagery (vs. 37% of adults), frequently describing fantastical creatures or expanded spaces.
These normally decrease after puberty as prefrontal cortex development enhances reality testing. Persistent frightening episodes may indicate nightmare disorder requiring professional evaluation.