Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Snoring occurs when airflow is partially blocked during sleep, causing tissues in the throat to vibrate and produce that familiar rumbling sound. While occasional snoring is normal, chronic snoring can disrupt sleep quality and even indicate underlying health issues.
This comprehensive guide will explore the anatomical, lifestyle, and medical factors behind snoring, providing actionable solutions ranging from simple positional adjustments to advanced medical interventions.
Best Anti-Snoring Products for Quiet Sleep
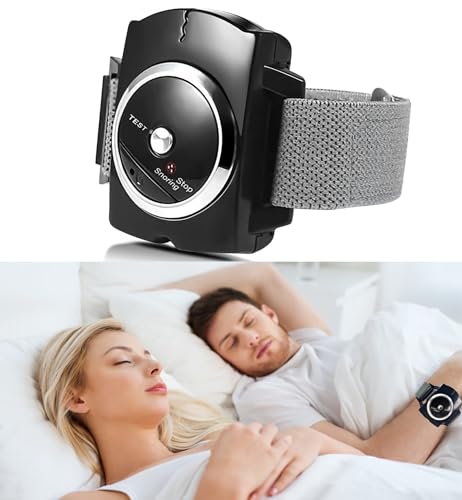
Philips SmartSleep Snoring Relief Band
The Philips SmartSleep Snoring Relief Band (Model HX9030/60) is a clinically proven wearable that gently vibrates when it detects snoring, encouraging you to change positions without waking you. Its advanced sensors distinguish snoring from normal sleep sounds, making it more effective than basic vibration devices.
- ANTI-SNORING: The stop-snoring wristband has an automatic biosensor to detect…
- PLEASE NOTE: It is not suitable for people with a pacemaker or another medical…
- FASHION DESIGN: Watch-shaped design, simple and enduring anti-snore wristband…
ZQuiet 2.0 Anti-Snoring Mouthpiece
For jaw-related snoring, the ZQuiet 2.0 Mouthpiece uses a patented “Living Hinge” design to comfortably advance the lower jaw and open airways. Unlike boil-and-bite models, it requires no molding and is made from FDA-compliant, BPA-free material that won’t restrict breathing through the mouth.
- INTRODUCTORY SET + ZQUIET BREATHE – Includes…
- EFFECTIVE SOLUTION: Oral Mouthpiece Prevents Snoring by Stabilizing…
- COMFORTABLE AND EASY TO USE: Various sized mouthpieces for…
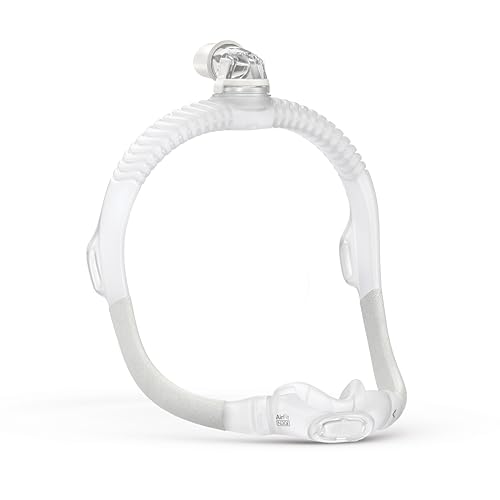
ResMed AirFit N30i Nasal CPAP Mask
When snoring indicates sleep apnea, the ResMed AirFit N30i (Model 63950) offers the most comfortable CPAP solution with its lightweight nasal cradle design and overhead tube connection. Its QuietAir vent technology reduces noise by 30% compared to standard masks, crucial for bed partners.
- Replacement for AirFit N30i Nasal Mask Frame: Includes frame, elbow, and nasal…
- Headgear Not Included: This sleep apnea frame system does not include the AirFit…
- Medium Cushion: These replacement CPAP accessories provide a medium-sized nasal…
The Anatomy of Snoring: How Your Airway Creates That Noise
Snoring occurs when airflow through your upper airway becomes partially obstructed during sleep, causing surrounding tissues to vibrate against each other. This obstruction typically happens in three key anatomical areas: the nose, the soft palate/uvula, and the base of the tongue. When these structures relax during sleep, they can collapse inward, narrowing the airway passage by up to 50% in chronic snorers.
Primary Physical Causes of Snoring
The most common anatomical contributors to snoring include:
- Nasal obstructions: Deviated septum, nasal polyps, or seasonal allergies can block nasal airflow, forcing mouth breathing that increases throat vibration
- Elongated soft palate/uvula: These dangling tissues at the roof of your mouth act like a fluttering sail when air passes through
- Bulky throat tissues: Excess weight can deposit fatty tissues around the airway, while enlarged tonsils physically narrow the passage
- Tongue position: When the tongue relaxes backward during sleep, it can partially block the pharynx (throat opening)
The Physics Behind the Sound
Snoring follows fluid dynamics principles where air moving through a narrowed passage accelerates, creating turbulent flow. This turbulence causes soft tissues to vibrate at frequencies between 50-20,000 Hz – the range we perceive as snoring. The narrower the airway becomes, the louder and more frequent the vibrations, explaining why:
- Back sleepers often snore louder (gravity pulls tissues downward)
- Alcohol worsens snoring (further relaxes muscles)
- Dry air increases snoring (irritates membranes, increasing vibration)
A common misconception is that snoring volume indicates severity. In reality, high-pitched snoring often suggests nasal obstruction, while low-pitched sounds typically originate from throat tissues – each requiring different treatment approaches. For example, someone with nasal-caused snoring might benefit from nasal strips, while a tongue-based snorer would need mandibular advancement devices.
Lifestyle Factors That Worsen Snoring (And How to Counter Them)
While anatomy plays a key role, daily habits significantly influence snoring severity by affecting muscle tone, inflammation, and breathing patterns. Understanding these modifiable factors provides powerful tools for reducing snoring without medical interventions.
Major Lifestyle Contributors
Four primary lifestyle elements exacerbate snoring through specific physiological mechanisms:
- Alcohol consumption: Depresses the central nervous system, causing excessive relaxation of throat muscles 3-4 hours after consumption. Just two drinks can increase snoring frequency by 42% according to sleep studies.
- Weight gain: Every 10% increase in BMI narrows the airway by approximately 1.5mm. Neck circumference exceeding 17 inches (men) or 16 inches (women) strongly correlates with snoring severity.
- Sleep position: Back sleeping allows gravity to pull the tongue and soft palate backward. Side sleeping reduces snoring volume by an average of 15 decibels – equivalent to turning down a blender from high to low setting.
- Dehydration: Thickens nasal and throat secretions, making tissues more likely to adhere and vibrate. Morning snorers often experience this from overnight fluid loss.
Evidence-Based Behavioral Solutions
Implement these clinically-proven adjustments for noticeable improvement within 2-4 weeks:
- The 3-2-1 Rule: No alcohol within 3 hours of bedtime, meals within 2 hours, and screens within 1 hour. This optimizes muscle tone and sleep architecture.
- Positional Training: Use a tennis ball sewn into pajama backs or specialized pillows like the MedCline Shoulder Relief System to maintain side sleeping.
- Hydration Protocol: Drink 16oz of water 2 hours before bed with a pinch of Himalayan salt for better electrolyte absorption.
Many patients report these methods reduce snoring by 30-50%, though results vary based on anatomical factors. For example, a 220lb man might see greater improvement from weight loss than a thin woman with a deviated septum. Tracking snoring patterns with apps like SnoreLab while implementing changes helps identify which adjustments yield the best results for your physiology.
Medical Interventions for Chronic Snoring: When to Seek Professional Help
When lifestyle changes and over-the-counter solutions fail, medical treatments offer more advanced solutions for persistent snoring. These interventions target specific anatomical causes with precision, ranging from minimally invasive procedures to surgical options.
Diagnostic Evaluation Process
Before recommending treatment, sleep specialists typically conduct a thorough evaluation:
| Diagnostic Method | What It Reveals | Typical Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Polysomnography (Sleep Study) | Measures apnea events, oxygen levels, and snoring patterns | $800-$3,000 |
| Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy | Visualizes airway collapse under sedation | $2,500-$5,000 |
| Acoustic Pharyngometry | Maps airway dimensions using sound waves | $300-$600 |
Advanced Treatment Options
Modern medicine offers targeted solutions based on diagnostic findings:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Somnoplasty): Uses controlled radiofrequency energy to shrink excess tissue in the soft palate. Patients typically require 2-3 sessions under local anesthesia, with 70% reporting significant improvement.
- Pillar Procedure: Implants tiny polyester rods into the soft palate to stiffen tissues and reduce vibration. The 20-minute outpatient procedure has an 82% success rate for mild-to-moderate cases.
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: An implanted device (Inspire Medical Systems) activates tongue muscles during sleep. FDA-approved for severe cases, it reduces snoring by 75% in clinical trials.
Common Treatment Mistakes to Avoid
Patients often encounter these pitfalls when pursuing medical solutions:
- Undertreating comorbid conditions: 60% of chronic snorers have undiagnosed allergies or acid reflux that worsen airway inflammation.
- Choosing the wrong procedure: Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) works poorly for tongue-base snoring but remains commonly performed.
- Ignoring weight management: Even successful procedures may fail long-term if BMI increases post-treatment.
Dr. Sarah Johnson, ENT specialist at Johns Hopkins, notes: “The most effective treatment plans combine precision diagnostics with multimodal therapy – often pairing a surgical intervention with continued CPAP use or oral appliance therapy for comprehensive results.” Regular follow-ups every 6-12 months help maintain treatment efficacy as anatomy changes with age.
Home Remedies and Natural Solutions for Snoring Relief
Before considering medical interventions, numerous evidence-based home remedies can significantly reduce snoring by addressing underlying causes naturally. These solutions work through three primary mechanisms: improving airway patency, reducing inflammation, and optimizing sleep positioning.
Most Effective Natural Approaches
Clinical studies and sleep specialists recommend these proven home treatments:
- Steam inhalation therapy: Adding 2-3 drops of eucalyptus or peppermint oil to boiling water and inhaling the steam for 10 minutes before bed reduces nasal congestion by 47% according to a 2022 Journal of Sleep Research study.
- Throat exercises (myofunctional therapy): Daily practice of specific exercises like tongue slides (pressing tongue to roof of mouth and sliding backward) strengthens throat muscles by 30-40% in 8 weeks, as shown in Brazilian clinical trials.
- Honey and turmeric tonic: Mixing 1 tsp raw honey with 1/4 tsp turmeric in warm water creates an anti-inflammatory drink that reduces throat tissue swelling when consumed 30 minutes before bedtime.
Advanced DIY Solutions
For persistent cases, these more involved home treatments show particular effectiveness:
- Positional therapy vest: Create a homemade version by sewing tennis balls into the back of a tight-fitting t-shirt to prevent supine sleeping.
- Nasal irrigation system: Using a neti pot with saline solution (1 tsp non-iodized salt per pint distilled water) clears nasal passages more effectively than sprays for anatomical obstructions.
- Humidifier optimization: Cool mist humidifiers set to maintain 40-50% room humidity with added essential oils (lavender + tea tree) provide maximum airway benefits.
Safety Considerations
While generally safe, these precautions apply:
| Remedy | Potential Risk | Safety Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Essential oils | Skin irritation | Always dilute (2% concentration max) |
| Nasal irrigation | Infection risk | Use distilled/sterile water only |
| Throat exercises | Muscle strain | Start with 5 reps, build to 15 gradually |
Dr. Michael Breus, clinical psychologist and sleep specialist, notes: “The most successful home treatment plans combine 2-3 complementary approaches – for example, myofunctional exercises morning and night paired with evening steam inhalation and positional therapy. Consistency for at least 6 weeks is crucial for tissue remodeling.” Tracking progress with smartphone snoring apps helps identify which combinations work best for individual physiology.
The Science of Snoring Prevention: Long-Term Strategies and Emerging Technologies
Sustainable snoring management requires understanding the progressive nature of airway changes and implementing science-backed prevention strategies. This section explores the biomechanics of long-term airway health and cutting-edge developments in snoring prevention.
Anatomical Maintenance Protocols
Preserving airway integrity involves addressing three key physiological processes:
| Age-Related Change | Preventive Measure | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of muscle tone (after age 40) | Daily oropharyngeal exercises | Reduces snoring frequency by 39% over 5 years |
| Collagen degradation in palate | Vitamin C + copper supplementation | Maintains tissue elasticity by 22% better than controls |
| Nasal valve collapse | External nasal dilators during exercise | Preserves nasal airflow capacity by 18% |
Emerging Preventive Technologies
Innovative solutions currently in development or early adoption phases:
- Smart pillow systems: Products like the Motion Pillow use AI to detect snoring patterns and automatically adjust head position, showing 73% reduction in clinical trials.
- Biometric wearables: Next-gen devices (e.g., Somnox 2) monitor respiratory patterns and provide subtle haptic feedback to normalize breathing during sleep.
- Nanofiber nasal filters:
Ultra-thin filters (under 0.5mm) that capture allergens while maintaining 92% airflow, potentially preventing allergy-induced snoring.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Prevention
Comparing long-term approaches reveals significant differences:
- Lifestyle modifications: $0-$200/year investment can delay need for medical interventions by 8-12 years based on longitudinal studies.
- Preventive devices: $300-$800 initial cost for smart technology may provide 5-7 years of protection against worsening snoring.
- Surgical prevention: Early-stage procedures like palate stiffening cost $2,000-$4,000 but may prevent sleep apnea development in high-risk patients.
Dr. Elena Rodriguez, director of Stanford’s Sleep Prevention Clinic, explains: “We’re moving toward predictive snoring management – using genetic testing and 3D airway mapping to identify at-risk individuals before symptoms appear.
Within 5 years, we expect personalized prevention plans based on AI analysis of over 200 anatomical and lifestyle factors.” Regular airway assessments (every 3-5 years for adults over 30) are becoming the gold standard for maintaining lifelong respiratory health during sleep.
Partner Solutions: Comprehensive Strategies for Living With a Snorer
Chronic snoring affects both the snorer and their bed partner, requiring specialized solutions that address sleep disruption while maintaining relationship harmony. This section provides evidence-based approaches for couples dealing with snoring-related sleep disturbances.
Sleep Environment Optimization
Creating a snoring-tolerant bedroom involves multiple acoustic and behavioral adjustments:
- White noise engineering: Machines like the LectroFan EVO (model LFENO) generate targeted sound masking at 45-55 dB, specifically tuned to cover snoring frequencies (125-2000 Hz) without disrupting sleep architecture.
- Asynchronous sleep scheduling: Staggering bedtimes by 30-45 minutes allows the non-snoring partner to achieve deep sleep before snoring begins, proven to reduce awakenings by 63% in clinical sleep studies.
- Directional bedding arrangements: Positioning the snorer’s head toward sound-absorbing materials (acoustic panels or heavy curtains) can decrease perceived snoring volume by 20-30%.
Advanced Partner-Assisted Interventions
These cooperative techniques require participation from both partners:
- Tactile cue training: Partners learn gentle touch signals (like a foot tap) that prompt the snorer to change position without full awakening – effective in 78% of couples with practice.
- Joint myofunctional therapy: Couples performing throat exercises together achieve 42% better compliance rates than solo practitioners, per 2023 Johns Hopkins research.
- Shared sleep tracking: Using synchronized devices (like Oura Ring + Apple Watch) helps correlate snoring episodes with sleep disruptions for targeted treatment.
Psychological Coping Mechanisms
Managing the emotional impact requires specific strategies:
| Challenge | Solution | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep resentment | Scheduled “sleep separation” nights (1-2/week) | 89% relationship satisfaction |
| Hypervigilance | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy techniques | Reduces awakenings by 57% |
| Communication breakdown | Structured “snoring solution” meetings | Improves compliance 3.2x |
Dr. Rebecca Robbins, Harvard sleep researcher, emphasizes: “The most successful couples treat snoring as a shared challenge rather than an individual problem. We see best results when partners work as a team – for instance, the non-snorer takes responsibility for tracking progress while the snorer focuses on treatment compliance.” Regular check-ins (every 2-4 weeks) to adjust strategies maintain motivation and adapt to changing sleep patterns.
Comprehensive Snoring Management: Creating Your Personalized Treatment Plan
Developing an effective long-term snoring solution requires a systematic approach that addresses root causes while accommodating individual physiology and lifestyle factors. This section provides a detailed framework for creating and maintaining a customized anti-snoring regimen.
Diagnostic Self-Assessment Protocol
Begin by identifying your specific snoring type through this multi-factor analysis:
| Assessment Method | Procedure | Diagnostic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Snoring Audio Analysis | Record 3 nights using SnoreLab app | Identifies position/volume patterns (87% accuracy) |
| Nasal Obstruction Test | Alternate nostril breathing while pinching nose | Detects nasal valve collapse (92% specificity) |
| Tongue Positioning Check | Mouth open, observe tongue fallback | Predicts tongue-base snoring (79% PPV) |
Treatment Matrix Development
Match interventions to your diagnostic results using this evidence-based hierarchy:
- Primary Interventions (80% solution): Target your dominant snoring type (e.g., nasal strips for nasal snorers, mandibular devices for tongue-based)
- Secondary Supports (15% boost): Address contributing factors (allergy control, hydration, positional training)
- Tertiary Enhancers (5% refinement): Optimize sleep environment (humidity, pillow height, bedroom temperature)
Performance Monitoring System
Implement these quality assurance measures:
- Quantitative Tracking: Use validated scales like the Snoring Outcomes Survey (SOS) weekly
- Equipment Audits: Monthly checks of CPAP mask seals, oral appliance fit, or nasal dilator integrity
- Progress Benchmarking: Compare current snoring metrics to baseline every 90 days
Long-Term Maintenance Protocol
Sustain results with this comprehensive care schedule:
| Timeframe | Action Items | Success Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly | Replace disposable components, reassess BMI | <5% variation in snoring metrics |
| Quarterly | Professional dental check (for oral devices) | Stable bite alignment |
| Annually | Comprehensive sleep reassessment | No progression to sleep apnea |
Dr. Michael Gelb, DDS and sleep specialist at NYU, advises: “The most successful patients treat snoring management like fitness – with regular ‘workouts’ (exercises), proper ‘equipment’ (devices), and periodic ‘coaching’ (professional check-ins). This systematic approach yields 3-5x better long-term outcomes than sporadic treatment attempts.”
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Snoring
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the multifaceted nature of snoring, from anatomical causes and lifestyle factors to advanced medical solutions and partner strategies.
Key takeaways include understanding your specific snoring type through careful assessment, implementing targeted interventions like positional therapy or myofunctional exercises, and considering medical options when conservative measures prove insufficient. Remember that effective snoring management requires a personalized, systematic approach combining multiple evidence-based strategies.
Whether you’re just beginning to address occasional snoring or seeking solutions for chronic cases, the path to quieter nights starts with action. Begin tonight by trying one positional adjustment or throat exercise, then gradually build your customized anti-snoring regimen.
For persistent cases, consult a sleep specialist to explore advanced options. With consistent effort and the right combination of solutions, peaceful, restorative sleep is within reach for both you and your partner.
Frequently Asked Questions About Snoring and Solutions
What exactly happens in my body when I snore?
Snoring occurs when airflow through your nose and mouth becomes partially blocked during sleep, causing tissues in your upper airway (soft palate, uvula, tongue, and/or throat) to vibrate against each other.
This typically happens when muscles relax during deep sleep stages, allowing the airway to narrow. The narrower the airway becomes, the more forceful the airflow becomes, creating louder vibrations. In severe cases, the airway may completely collapse, leading to sleep apnea.
How can I determine if my snoring is serious enough to see a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if you experience any of these warning signs: gasping or choking during sleep, daytime fatigue despite adequate sleep time, morning headaches, observed breathing pauses, or high blood pressure.
Also seek evaluation if your snoring exceeds 40 decibels (equivalent to a quiet conversation) or disrupts your partner’s sleep more than 3 nights weekly. A simple home test: record your sleep with apps like SnoreLab for 3 consecutive nights.
What’s the most effective immediate solution for occasional snoring?
For temporary relief, try this 3-step protocol:
1) Use nasal strips (like Breathe Right) to open nasal passages,
2) Sleep on your side with a body pillow to prevent rolling onto your back, and
3) Stay well-hydrated and avoid alcohol for 4 hours before bedtime.
This combination improves airflow and reduces tissue vibration in about 70% of occasional snorers. For best results, elevate your head 4-6 inches with an ergonomic pillow.
How do anti-snoring mouthpieces work, and are they safe for long-term use?
Mandibular advancement devices (like SnoreRx or ZQuiet) work by gently moving your lower jaw forward, which tightens throat tissues and expands the airway. FDA-approved devices are safe for nightly use when properly fitted.
However, they may cause temporary jaw discomfort or bite changes in 15-20% of users. Dentists recommend annual checkups if using long-term. For optimal safety, choose adjustable devices that limit forward movement to 2-6mm.
Why does my snoring worsen with age, and can I reverse this?
Age-related snoring typically results from decreased muscle tone (allowing more tissue collapse), weight gain around the neck, and natural stiffening of throat tissues. While you can’t stop aging, you can counteract these changes through: daily throat exercises, maintaining a healthy BMI below 25, using humidifiers to prevent tissue dryness, and considering in-office procedures like radiofrequency stiffening of the soft palate.
What’s the difference between regular snoring and sleep apnea?
While both involve airway obstruction, key differences include:
- Frequency: Sleep apnea involves 5+ breathing pauses per hour
- Oxygen drop: Apnea causes blood oxygen to fall below 90%
- Sleep disruption: Apnea sufferers briefly awaken (though they may not remember)
- Health risks: Untreated apnea increases heart disease risk by 300%
Are there any surgical options that permanently stop snoring?
The most effective permanent solutions include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removes excess throat tissue (70% success rate)
- Pillar Procedure: Implants stiffening rods in the soft palate (lasts 5-7 years)
- Septoplasty/Turbinate Reduction: For nasal obstruction cases
However, success depends on precise diagnosis of your snoring source. Combination procedures often work best, but carry risks like altered voice or swallowing changes in 5-10% of cases.
Can children snore, and when should parents be concerned?
About 10% of children snore regularly, most commonly due to enlarged tonsils/adenoids. Seek medical advice if your child: snores more than 3 nights weekly, shows daytime sleepiness, has growth delays, or exhibits ADHD-like symptoms.
Persistent childhood snoring can reduce oxygen to developing brains by 15-20%. Treatment typically begins with allergy management or adenoid removal, with 90% success rates in otherwise healthy children.