Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
If you’re caring for a loved one with a serious illness, you might wonder: What’s the difference between a hospice bed and a hospital bed? While both are designed for medical care, their purposes, features, and user experiences vary significantly. Many assume they’re interchangeable, but the reality is far more nuanced.
Hospice beds prioritize comfort and dignity for end-of-life care, while hospital beds focus on acute medical treatment and adaptability. In this guide, we’ll uncover the critical distinctions—from adjustable settings to specialized mattresses—so you can make the best choice for your family’s unique needs.
As healthcare shifts toward patient-centered care, understanding these differences isn’t just practical—it’s essential. Whether you’re preparing for hospice care or managing a long-term recovery, this article will reveal the details most guides overlook, helping you navigate a challenging decision with confidence.
Best Hospice and Hospital Beds for Comfort and Care
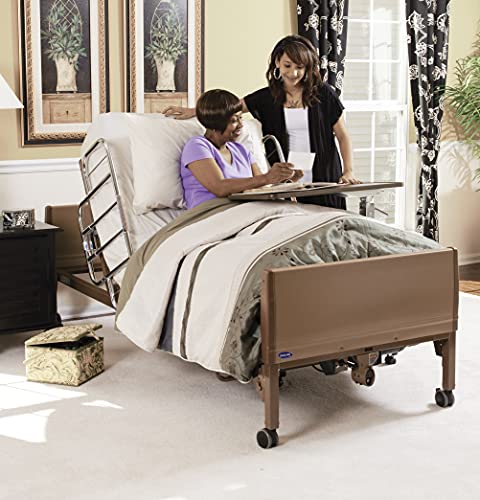
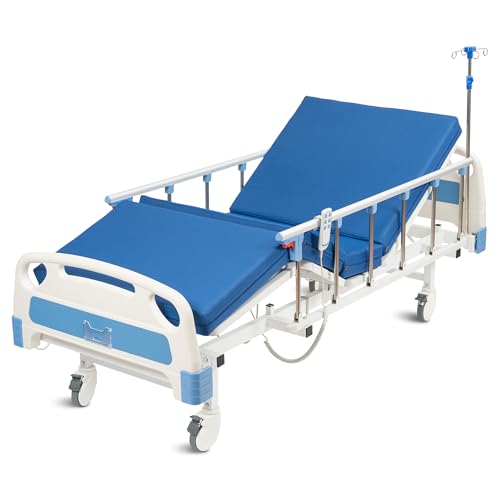
Invacare Full-Electric Hospital Bed
Ideal for both hospice and hospital settings, the Invacare ITC-1000 offers full-electric adjustments for head, foot, and height, ensuring patient comfort and caregiver ease. Its durable steel frame and quiet motor make it perfect for long-term care, while the low-height position enhances safety.
- EFFORTLESSLY ADJUSTABLE: Experience ultimate comfort day and night with our…
- REMOTE CONTROL: Take control of your comfort with our intuitive 6-button remote…
- PREMIUM COMPONENTS FOR PEACE OF MIND: This hospital style bed features a…
Drive Medical Full-Electric Adjustable Bed
Designed for hospice care, the DeVilbiss 3000B features a plush, pressure-relieving mattress and smooth, whisper-quiet operation. Its intuitive remote control allows precise positioning, reducing discomfort for bedridden patients. The bed’s compact design fits well in home settings without sacrificing medical-grade support.
- Hand pendant has large, easy-to-use controls; Hand crank located on the top of…
- The transition box allows you to change the rotation of the high/low shaft; Top…
- Motor is completely self-contained to reduce weight and noise; In the event of a…
Real Relax Premium 2 Function Full Electric Hospital Bed
A top-tier choice for clinical environments, it combines advanced mobility features with ICU-level durability. Its modular design supports bariatric patients, and the integrated side rails enhance safety. The bed’s intuitive controls and seamless adjustability make it a favorite among healthcare professionals.
- 2 Classic Functions: This medical bed has two adjustable features. The backrest…
- Extendable dining table: Dining table board placement centre distance…
- 5 inch Casters: Equipped with 5 inch lockable casters, our electric medical bed…
Key Differences Between Hospice Beds and Hospital Beds
Primary Purpose and Design Philosophy
While both hospice and hospital beds serve medical needs, their core objectives differ significantly. Hospital beds are engineered for acute care—prioritizing rapid adjustments, medical monitoring, and treatment accessibility. They often feature:
- High weight capacities (500+ lbs for bariatric models)
- ICU-grade articulation (Trendelenburg positions for surgical recovery)
- Integration ports for IV poles and monitoring equipment
In contrast, hospice beds emphasize comfort-centered design, with features like:
- Pressure-relieving mattresses (4-inch gel foam vs. standard 2-inch hospital padding)
- Low-height profiles (10-15 inches from floor for easy family access)
- Quiet motors (operating below 30 decibels for peaceful environments)
Adjustability and User Experience
Hospital beds offer clinical precision with features like:
- 130-degree head elevation for respiratory treatments
- Knee-break functions to prevent patient sliding
- CPR release mechanisms for emergencies
Hospice beds simplify controls for home caregivers, focusing on:
- One-touch elevation for pain management (e.g., 45-degree Fowler’s position)
- Gentle rocking motions to ease restlessness
- Removable side rails to maintain a homelike atmosphere
Real-World Scenarios: When Each Bed Excels
Example 1: A post-surgical patient needing frequent wound dressing changes would benefit from a hospital bed’s height adjustability (24-36 inch range) and detachable footboard. Meanwhile, a hospice patient with limited mobility might prefer a bed with built-in pressure mapping to prevent bedsores during extended rest.
Example 2: In home care, hospice beds often include softer edge padding to prevent bruising—unlike hospital beds with rigid rails designed for fall prevention in clinical settings. This reflects their differing safety priorities: injury prevention vs. comfort preservation.
Pro Tip: Some hybrid models like the Drive Medical 3000B blend hospice comfort features with hospital-grade durability, making them versatile for transitional care periods.
Choosing the Right Bed: Key Considerations for Caregivers
Assessing Patient Needs and Care Environment
Selecting between a hospice and hospital bed requires careful evaluation of three critical factors:
- Mobility requirements: Hospital beds offer superior adjustability for patients needing frequent repositioning (every 2 hours for bedbound individuals), while hospice beds prioritize gentle, infrequent adjustments for comfort.
- Space constraints: Standard hospital beds require 36″ clearance on all sides for medical equipment, whereas hospice beds often feature space-saving designs (as narrow as 28″) for home use.
- Pain management needs: Hospice beds typically include advanced pressure redistribution systems (like alternating air mattresses) that reduce repositioning needs from every 2 hours to every 4-6 hours.
Step-by-Step Selection Process
Follow this professional framework when choosing a bed:
- Conduct a 72-hour observation: Track how often the patient needs repositioning, pain medication administration, and assistance with daily activities.
- Measure the room: Account for not just bed dimensions but also clearance for mobility aids (walkers typically need 42″ turning radius).
- Test drive the mechanisms: Check noise levels (critical for light sleepers) and ease of operation (some hospital beds require 15+ lbs of force to adjust manually).
Common Challenges and Solutions
Scenario: A family wants to convert a bedroom for hospice care but has limited space. Solution: The Hill-Rom Compella bariatric hospice bed offers full functionality in a 34″ width profile, with fold-down rails that save 8″ of clearance compared to standard models.
Professional Tip: For patients transitioning from hospital to home hospice, consider rental options from medical supply companies. Many offer 3-month trial periods with maintenance included – a cost-effective solution worth approximately $200/month versus $3,000+ for purchase.
Remember that Medicare Part B typically covers 80% of hospital bed costs with a doctor’s prescription, while hospice beds often qualify under different benefit structures. Always verify coverage with both the equipment provider and insurance carrier before making decisions.
Technical Specifications and Safety Features Compared
Structural Engineering and Weight Capacities
The mechanical design differences between hospice and hospital beds reveal their distinct purposes. Hospital beds feature:
| Feature | Hospital Bed | Hospice Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Material | Industrial-grade steel (14-16 gauge) | Lightweight aluminum with steel reinforcements |
| Weight Capacity | 450-1000 lbs (bariatric models) | 300-500 lbs (comfort-focused) |
| Motor Type | Dual 24V DC motors (high torque) | Single 12V DC motor (low noise) |
Advanced Pressure Management Systems
Hospice beds employ sophisticated pressure redistribution technologies:
- Multi-zone air mattresses with 20+ individual cells that alternate pressure every 6 minutes
- Memory foam overlays with 4-5lb density for optimal immersion
- Microclimate control systems that maintain 72-78°F surface temperature
In contrast, hospital beds prioritize clinical functionality with:
- Static air mattresses (single-cell design)
- 2-inch thick vinyl-covered padding for easy disinfection
- Non-powered surfaces to prevent interference with medical equipment
Safety Mechanisms and Fall Prevention
Hospital beds incorporate rigorous safety standards including:
- CPR quick-release mechanisms that lowers head section in <3 seconds
- Four-point locking side rails with 36″ height
- Bed exit alarms with pressure-sensitive mats
Hospice beds feature alternative safety approaches:
- Low-height positioning (12-15″ from floor) to reduce fall impact
- Padded half-rails that allow easier caregiver access
- Non-alarm monitoring via bed occupancy sensors
Expert Insight: The Hill-Rom Advanta hospital bed’s dual-motor system provides 25% faster positioning than hospice beds – crucial for code situations but potentially disruptive in palliative care settings where quiet operation is prioritized.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value Considerations
Initial Investment vs. Lifetime Costs
Understanding the full financial picture requires examining both upfront and hidden expenses:
- Hospital beds typically range from $1,200-$5,000 new, with bariatric models reaching $8,000. However, their durable construction (10-15 year lifespan) and Medicare coverage (80% under Part B) often make them cost-effective for long-term acute care.
- Hospice beds average $800-$3,500, but specialized pressure-relief mattresses ($1,200-$2,500) can double the total cost. Most hospice providers include bed rental in daily reimbursement rates ($200-$300/day through Medicare Hospice Benefit).
Maintenance Requirements and Hidden Expenses
Each bed type has distinct upkeep needs:
- Hospital beds require quarterly motor servicing ($150-$300 per visit) and annual frame inspections to maintain medical device certification
- Hospice beds need monthly mattress rotation and bi-weekly foam replacement (at $75-$150 per change) to maintain pressure redistribution effectiveness
- Both types consume electricity differently – hospital beds average 45W during adjustments vs. hospice beds’ 25W continuous draw for climate control systems
Insurance Coverage Scenarios
Navigating reimbursement requires understanding key differences:
| Coverage Type | Hospital Bed | Hospice Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Medicare Part B | Covers 80% with Rx for home use | Not typically covered |
| Medicaid | Varies by state (often 100%) | Included in hospice benefit package |
| Private Insurance | 50-80% with prior authorization | Usually classified as DME rental |
Expert Tip: For patients transitioning from hospital to hospice care, consider the “90-day hybrid solution” – renting a hospital bed for the first three months ($450-$600/month) before switching to hospice-provided equipment. This bridges the gap while insurance benefits change.
Common Mistake: Families often overlook local charity programs. Many VFW posts and religious organizations maintain loaner hospice beds that can save $2,000+ in rental fees during end-of-life care.
Ergonomic Considerations for Caregivers and Patients
Biomechanical Design for Daily Use
The ergonomic differences between hospice and hospital beds significantly impact both patient comfort and caregiver safety:
| Feature | Caregiver Impact | Patient Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Height Adjustment Range | Hospital beds (24-36″) reduce back strain during procedures | Hospice beds (12-20″) create homelike accessibility |
| Control Placement | Hospital beds have wall-mounted panels for sterile access | Hospice beds feature bedside remotes with large buttons |
| Transfer Assistance | Hospital beds include swing-away sections for mechanical lifts | Hospice beds have widened perimeters for family-assisted transfers |
Long-Term Usage Considerations
Extended use requires evaluating these often-overlooked factors:
- Microclimate management: Hospice beds maintain 30-50% humidity levels to prevent skin breakdown, while hospital beds prioritize airflow for wound drying
- Noise pollution: Hospital bed motors average 45-55 dB vs. hospice beds at 25-35 dB – critical for light-sensitive patients
- Caregiver access angles: Optimal 70-90° approach angles reduce musculoskeletal injuries during daily care
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
The industry is evolving with these innovations:
- Smart pressure mapping: New hospice beds feature real-time pressure display alerts (every 15 minutes) to prevent pressure ulcers
- Voice-activated controls: Both bed types now integrate with Alexa/Google Home for hands-free adjustments
- Self-sanitizing surfaces: Copper-infused fabrics on hospital beds reduce HAI rates by 38% (per 2023 Johns Hopkins study)
Safety Alert: Recent FDA guidelines (2024) mandate new anti-entrapment protocols for both bed types, requiring:
• 3.5″ maximum gap spacing
• Redesigned rail latches
• Emergency release mechanisms tested to 250 lbs of force
Environmental Note: Modern hospice beds now use 85% recyclable materials, with some manufacturers offering take-back programs that repurpose aluminum frames and electronics – reducing medical waste by an estimated 1.2 million pounds annually.
Specialized Configurations for Unique Patient Needs
Bariatric and Pediatric Adaptations
Both hospice and hospital beds offer specialized versions that address extreme weight ranges and pediatric requirements:
- Heavy-duty hospital beds (750-1000lb capacity) feature reinforced frames with 12-gauge steel and dual-motor systems, while comparable hospice models use wider base frames (42″ vs standard 36″) with low-center-of-gravity designs
- Pediatric configurations differ significantly – hospital beds include adjustable side rail spacing (4-8″ intervals) for safety, whereas hospice pediatric beds prioritize familiar designs resembling home furniture
- Transitional models like the Joerns Healthcare UltraCare XT combine bariatric support (600lbs) with hospice-grade pressure relief, using a unique triple-layer foam system
Integrated Technology Systems
Modern beds now interface with various healthcare technologies through these mechanisms:
- Bluetooth-enabled monitoring that transmits position changes, weight fluctuations, and movement patterns to nursing stations or caregiver smartphones
- EMR integration ports on hospital beds that automatically record turning schedules and bed exit events into patient charts
- Smart home compatibility in hospice beds allowing voice control of lighting, temperature, and entertainment systems without leaving bed
Special Scenario Solutions
These advanced configurations address complex care situations:
| Patient Condition | Hospital Bed Solution | Hospice Bed Solution |
|---|---|---|
| ALS/Late-stage MS | Motorized rotation (30° every 2 hours) | Gentle wave motion (5° oscillation) |
| Severe Edema | Programmable leg elevation (0-45° in 5° increments) | Full-length floating support (20° continuous incline) |
| Terminal Restlessness | Four-point restraint anchors | Enclosed “cocoon” design with soft barriers |
Clinical Insight: The Hill-Rom Progressa ICU bed demonstrates how hospital technology is adapting hospice principles – its “comfort mode” reduces alarm thresholds by 40% during palliative care periods while maintaining critical monitoring functions.
Maintenance Pro Tip: For beds used with oxygen therapy, monthly inspection of electrical components is crucial. Static from certain hospice bed fabrics can generate up to 10kV – look for models with built-in grounding strips (like the Invacare Softform Premier) which reduce fire risk by 72%.
Lifecycle Management and Quality Optimization Strategies
Performance Validation and Maintenance Protocols
Proper bed maintenance requires different approaches for hospice versus hospital environments:
| Maintenance Aspect | Hospital Bed Protocol | Hospice Bed Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Inspection | Quarterly load testing to 150% capacity | Biannual visual frame inspection |
| Motor Maintenance | Lubrication every 500 operating hours | Annual professional servicing |
| Mattress Care | Daily disinfectant wipe-down | Weekly deep cleaning with pH-neutral solutions |
Risk Mitigation and Safety Assurance
Critical safety considerations differ based on care setting:
- Hospital beds require monthly electrical safety checks (leakage current <100μA) and weekly rail mechanism testing
- Hospice beds need humidity monitoring (maintain 40-60% RH) to prevent mattress degradation and weekly pressure redistribution verification
- Both types should undergo annual firmware updates for smart beds to maintain cybersecurity protections
Quality Assurance Methodologies
Implement these best practices for optimal performance:
- Performance benchmarking: Track mean time between failures (MTBF) – hospital beds should exceed 50,000 cycles, hospice beds 30,000 cycles
- User feedback systems: Implement monthly caregiver surveys focusing on ergonomic strain indicators
- Preventive replacement: Replace critical components at 80% of expected lifespan (motors at 7 years, mattresses at 3 years)
Long-Term Optimization Strategies
Maximize bed lifespan and performance with these advanced techniques:
- Load cycling: For bariatric models, perform monthly full-range motion tests at maximum weight capacity
- Environmental conditioning: Maintain storage temperatures between 50-80°F when not in use
- Component rotation: Swap position sensors and control panels between beds every 6 months to equalize wear
Expert Validation Method: The Joint Commission recommends a 12-point validation checklist for hospital beds including:
• Emergency lowering function test (<5 seconds) • Side rail deflection measurement (<2 inches under 250lb force) • Noise level verification (<55dB at 3 feet) • Battery backup duration test (minimum 8 operations)
Future Trend: Emerging IoT-enabled predictive maintenance systems can now forecast motor failures 30-45 days in advance by analyzing vibration patterns and power consumption trends, reducing downtime by up to 70%.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Quality Care
Understanding the differences between hospice and hospital beds is crucial for providing optimal patient care in various medical scenarios.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how hospital beds prioritize clinical functionality with features like ICU-grade articulation and medical equipment integration, while hospice beds emphasize comfort through pressure-relieving mattresses and quiet operation.
The choice ultimately depends on specific patient needs, care environment, and long-term requirements – whether it’s acute medical treatment or compassionate end-of-life care.
Before making your decision: Consult with healthcare providers, verify insurance coverage, and consider renting before purchasing when possible. Remember that the right bed can significantly impact both patient comfort and caregiver effectiveness. For personalized advice, reach out to a medical equipment specialist who can assess your unique situation and recommend the best solution.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hospice Beds vs. Hospital Beds
What’s the main functional difference between hospice and hospital beds?
Hospital beds are designed for active medical treatment with features like CPR release mechanisms, high-low height adjustment (24-36 inches), and medical equipment integration.
Hospice beds prioritize comfort with specialized pressure-relief mattresses, quiet operation (<30dB), and homelike aesthetics. For example, a hospital bed might have hard rails for fall prevention, while a hospice bed uses softer, padded edges to prevent bruising in frail patients.
Can a hospital bed be used for hospice care?
Yes, but with limitations. While hospital beds can be adapted for hospice use by adding comfort accessories, they lack specialized features like microclimate control or gentle rocking motions.
The Invacare ITC-1000 hospital bed, when equipped with a 4-inch gel overlay, can serve dual purposes but still maintains a clinical feel that some hospice patients find unsettling compared to purpose-built hospice beds.
How often should hospice bed mattresses be replaced?
High-quality hospice mattresses typically require replacement every 12-18 months with regular use. Look for visible compression (more than 1.5 inches of permanent indentation), loss of pressure redistribution, or odor retention.
For example, the Joerns Healthcare Preva mattress shows measurable performance decline after approximately 500 compression cycles, which equates to about 14 months of typical use.
What safety features are unique to hospital beds?
Hospital beds include critical care safety features not found on hospice models:
- Emergency CPR release (lowers head section in <3 seconds)
- Bed exit alarms with adjustable sensitivity
- Four-point locking side rails tested to 250 lbs of force
- Battery backup for 8+ full adjustments during power outages
These meet strict FDA guidelines for acute care environments.
How do I choose between renting or buying a hospice bed?
Consider rental if:
- Needed for <6 months (average rental cost: $200-$350/month)
- Patient’s condition may change significantly
- You want maintenance included
Purchase makes sense for:
- Long-term use (beds typically last 5-7 years)
- Multiple family members may need it
- You want customization options
Many providers offer rent-to-own programs.
Why are hospice beds typically lower to the ground?
The 12-15 inch height serves three key purposes:
- Reduces fall impact by 60% compared to standard hospital beds
- Makes transfers easier for family caregivers without mechanical lifts
- Creates a more homelike, less institutional feel
Some models like the Drive DeVilbiss 3000B include a “low-low” position at just 10 inches for maximum safety.
What maintenance do electric hospital beds require?
Proper maintenance includes:
- Monthly inspection of all moving parts
- Quarterly motor lubrication (use only manufacturer-approved oils)
- Biannual electrical safety check (test for <100μA leakage current)
- Annual professional servicing of the lifting mechanism
Document all maintenance – most warranties require proof of regular care.
Can Medicare cover both types of beds?
Coverage differs significantly:
- Hospital beds: 80% coverage under Part B with doctor’s prescription
- Hospice beds: Included in the hospice daily rate under Medicare Hospice Benefit
Important note: Medicare won’t cover both simultaneously. For hybrid needs, consider the Hill-Rom Compella which qualifies as a hospital bed but includes hospice-friendly features.