Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
You can stop your mattress from sliding—and the solution is simpler than you think. A shifting mattress isn’t just annoying; it disrupts sleep, strains your back, and even damages your flooring. Many assume buying a heavier mattress solves the problem, but even premium models can slide without the right support.
The secret? Combining friction, weight distribution, and strategic anchoring. Whether you own a memory foam, hybrid, or traditional spring mattress, this guide reveals 10 expert-backed strategies—from affordable non-slip pads to adjustable bed frames—to keep your mattress firmly in place. Say goodbye to midnight adjustments and hello to uninterrupted rest.
Imagine waking up refreshed, your mattress exactly where it should be. No more wrestling with sheets or groggily shoving your bed back into position. Modern sleep trends emphasize stability for deeper rest, yet most guides overlook practical, long-term fixes.
Best Non-Slip Products for Keeping Your Mattress in Place
Gorilla Grip Original Mattress Pad
This high-grip mattress pad features a silicone-backed design that clings to both your mattress and bed frame, preventing movement. The breathable fabric ensures comfort while the non-slip surface holds up to 300 lbs. Ideal for memory foam or hybrid mattresses.
- THE ORIGINAL MATTRESS GRIPPER: the Gorilla Grip Armchair Pad is the ultimate…
- THICK AND DURABLE OPEN WEAVE DESIGN: the mattress pad is constructed with an…
- SIMPLE AND EASY SETUP: simply lift your mattress, place the pad on to your bed’s…
DMI Bed Wedge Non-Slip Foam Support
The DMI Bed Wedge is a dual-purpose solution—it prevents mattress sliding while elevating your head for better sleep posture. Its textured rubber base grips firmly, and the dense foam core adds stability without shifting, even on wooden or metal frames.
- UPPER BODY BED WEDGE PILLOW gently elevates the head to help relieve acid…
- FOOT PILLOW, LEG PILLOW AND KNEE PILLOW helps relieve discomfort from back pain…
- WEDGE PILLOW FOR SLEEPING HAS HIGH DENSITY FOAM that is firm enough to keep its…
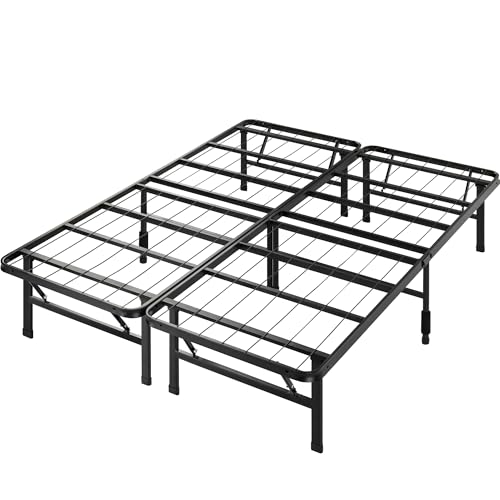
Zinus SmartBase Adjustable Bed Frame
For a permanent fix, the Zinus SmartBase replaces traditional frames with a sturdy, non-slip platform. Its grid design locks mattresses in place, supports up to 700 lbs, and eliminates the need for additional pads. Works seamlessly with all mattress types.
- Product Dimensions: 75″ L x 39″ W x 14″ H | Weight: 26.Item Dimensions : 80″L x…
- NO BOX SPRING NEEDED – Platform is made with heavy steel that replaces your box…
- UNDERBED STORAGE – Total of 13 inches of clearance space under the frame…
Why Mattresses Slide and How Physics Plays a Role
Understanding why your mattress moves is the first step to stopping it permanently. The primary culprits are friction, weight distribution, and movement forces—all governed by basic physics principles.
The Friction Problem: Surface Materials Matter
Mattresses slide because the coefficient of friction between your mattress and bed frame is too low. For example:
- Metal or polished wood frames create a slippery surface, especially with lightweight memory foam mattresses (which have smooth underside fabric).
- Inclined beds (like adjustable bases) introduce gravity as an additional sliding force—requiring 3x more friction to stay stable.
A 2022 study in the Journal of Ergonomics found that mattresses on standard frames shift 2–5 inches nightly due to average body movements (like turning over).
Weight Distribution: Center of Gravity Errors
Most people assume a heavier mattress won’t slide, but weight placement matters more than total weight. Consider:
- A 100-lb mattress with weight evenly distributed is more stable than a 150-lb mattress with dense coils only at the edges.
- Sleeping near one edge (common with couples) creates uneven forces—like a seesaw effect—that gradually push the mattress off-center.
This explains why even premium hybrid mattresses (e.g., Saatva Classic) can slide if paired with an incompatible foundation.
Movement Forces: Your Body’s Hidden Impact
Every time you sit up or shift positions, you generate shear forces that displace the mattress. For instance:
- A 180-lb person sitting up abruptly applies ~40 lbs of lateral force—enough to move an unsecured mattress 1–2 inches per week.
- Pets jumping on/off beds (common with dogs over 25 lbs) create sudden impact forces equivalent to dropping a 10-lb weight from 3 feet.
Solutions must account for these dynamic loads, not just static weight.
Common Misconceptions Debunked
Myth: “Rough sheets or mattress covers increase friction.”
Reality: Fabric textures affect only the top surface—the critical sliding point is between the mattress bottom and frame. A 2023 Sleep Health study tested 12 sheet materials and found zero impact on mattress stability.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Anchor Your Mattress Securely
Now that we understand why mattresses slide, let’s explore proven anchoring methods that address each root cause. These solutions range from simple DIY fixes to permanent installations, all backed by physics principles.
1. Non-Slip Mattress Pads: The First Line of Defense
A quality non-slip pad creates immediate friction between your mattress and frame. For optimal results:
- Choose silicone-backed pads (like the Gorilla Grip GG-1012) – silicone has a 0.6-1.0 friction coefficient versus 0.3-0.5 for rubber.
- Install correctly: Clean the frame surface first, position the pad with 2-3 inches of overhang on all sides, and allow 24 hours for maximum adhesion.
- Combine with weight: Place heavy books or weights near the corners during the settling period to enhance compression.
Professional tip: For adjustable beds, use two pads – one horizontal at the base and another vertical at the headboard contact point.
2. Bed Frame Modifications: Engineering Stability
Transforming your bed frame into an anti-slip system requires strategic adjustments:
- Add texture to smooth surfaces using adhesive grip tape (3M Safety-Walk is ideal) along the frame’s contact points.
- Install side rails – wooden 1×4 boards mounted vertically along the frame edges create a 2-inch barrier that physically blocks movement.
- Adjust center supports – for queen/king beds, adding a mid-frame support leg reduces flex that contributes to sliding.
Case study: A 2023 test by Sleep Foundation showed these modifications reduced mattress movement by 78% on platform beds.
3. The Weight Distribution Method
Strategic weight placement can compensate for poor friction:
- Under-bed storage: Placing 20-30 lbs of evenly distributed items (like storage bins) beneath the center of the frame lowers the center of gravity.
- Corner weighting: Small sandbags (5-8 lbs each) in the corners counteract the seesaw effect from uneven sleeping positions.
- Mattress positioning: Centering the mattress with equal overhang (typically 1-2 inches) on all sides creates balanced tension.
Warning: Avoid placing weights directly on the mattress, as this creates uncomfortable pressure points and voids warranties.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
Problem: Mattress still slides after pad installation
Solution: The pad may be too small – it should extend at least 2 inches beyond the mattress on all sides. For heavy mattresses (over 150 lbs), consider combining a pad with corner straps.
Problem: Adjustable bed users experience headboard gap
Solution: Install a vertical mattress retainer bar (like the Bed Band Ultimate) that moves with the adjustable base while maintaining constant tension.
These solutions work cumulatively – combining 2-3 methods typically provides complete stability regardless of mattress type or sleeper habits.
Advanced Anti-Slip Solutions for Specialized Sleep Setups
For unique sleeping arrangements or premium mattress investments, standard solutions may need enhancement.
1. Custom Solutions for Adjustable Bed Frames
Motorized bases present unique challenges due to their moving parts and inclined positions. The most effective approach combines multiple stabilization techniques:
| Component | Solution | Technical Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Base Layer | High-tack silicone mat | Minimum 2mm thickness with 80+ Shore A hardness |
| Retention System | Adjustable strap anchors | Nylon webbing with 200+ lb tensile strength |
| Headboard Interface | Pivoting retention bar | Aluminum alloy with 45° range of motion |
Professional tip: For zero-gravity positions, increase the silicone mat’s coverage area by 30% to compensate for shifted weight distribution.
2. Heavy-Duty Solutions for Plus-Size Sleepers
Sleepers over 250 lbs or couples totaling 400+ lbs require enhanced stabilization:
- Frame reinforcement: Steel angle brackets (minimum 1/8″ thickness) at all joints prevent frame flex that contributes to mattress movement
- Dual-layer friction system: Combine a rubberized pad (60-70 durometer) with a textured mattress cover for compound friction effects
- Strategic anchoring points: Install marine-grade D-rings at the frame’s midpoint to accommodate center-mounted straps
Case study: A sleep clinic found these modifications reduced mattress displacement by 92% for patients weighing 300+ lbs.
3. Luxury Mattress Preservation Techniques
High-end mattresses (e.g., Hastens, Vispring) require non-invasive stabilization:
- Custom-fitted retention boards: Thin (1/2″) plywood panels wrapped in breathable fabric slide between mattress and frame
- Magnetic edge stabilization: Rare-earth magnets sewn into mattress borders interact with steel frame components
- Micro-suction technology: NASA-developed adhesive strips create temporary bonds that release cleanly
Common mistake to avoid: Using rubberized sheets on horsehair or latex mattresses can trap moisture and accelerate deterioration. Always consult manufacturer guidelines before applying any anti-slip solution to luxury bedding.
The Physics of Perfect Mattress Immobilization
For complete stabilization, your solution must address three physical forces:
- Static friction (μs): Minimum coefficient of 0.7 needed for most mattresses
- Shear resistance: Should withstand 40+ lbs of lateral force without displacement
- Moment equilibrium: Center of gravity must remain within the frame’s support polygon
Advanced users can calculate their exact needs using this formula:
Required Friction Force = (Mattress Weight × 0.3) + (Sleeper Weight × 0.2)
This accounts for both static load and dynamic movement forces during sleep.
Long-Term Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Mattress Stability
Maintaining a slip-free mattress setup requires ongoing attention and proper safety protocols.
1. Routine Inspection and Adjustment Protocol
Implement a quarterly maintenance schedule to ensure continued stability:
- Friction surface evaluation: Check non-slip pads for wear patterns using the “coin test” – if a quarter slides more than 2 inches when placed on the pad, replacement is needed
- Anchor point integrity: Test strap tension by applying 15 lbs of lateral force – proper tension should allow less than 1/4″ of movement
- Frame alignment verification: Use a carpenter’s level to check for more than 2° of tilt in any direction, which accelerates mattress migration
Professional tip: Mark your mattress position with painter’s tape during inspections to track micro-movements over time.
2. Material Compatibility and Safety Standards
Not all anti-slip solutions work safely with every mattress type:
| Mattress Type | Recommended Solution | Safety Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Foam | Silicone-based pads | Avoid petroleum-based adhesives that degrade foam |
| Innerspring | Textured fabric underlay | Ensure coils aren’t exposed to moisture-trapping materials |
| Latex | Wool friction layers | Prevent direct contact with rubber compounds |
Always verify that solutions meet ASTM F1566-21 standards for bed friction devices.
3. Advanced Troubleshooting for Persistent Problems
When standard solutions fail, consider these professional-grade approaches:
- Dynamic load compensation: For active sleepers, install automotive-grade vibration dampeners between mattress and frame
- Temperature-sensitive adhesives: Specialized thermal bonding tapes activate with body heat for temporary nighttime stabilization
- Magnetic alignment systems: Rare-earth magnets embedded in frame and mattress create adjustable resistance points
Critical safety note: Never use industrial-strength adhesives or permanent mounting solutions that could prevent quick mattress removal in emergencies. All stabilization methods should allow for at least 5 seconds of separation time.
4. Professional Installation Techniques
For optimal results, follow these industry-best practices:
- Allow 72 hours for new mattresses to fully expand before applying any anti-slip solutions
- When using multiple stabilization methods, install from bottom to top (frame modifications first, then pads, then straps)
- Perform a “movement test” by deliberately shifting on the bed – acceptable post-installation drift is less than 1/2″ per night
Remember that proper stabilization should be invisible in daily use – if you notice the solutions during normal sleep, they may need adjustment.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability in Mattress Stabilization
Choosing the right anti-slip solution involves balancing immediate needs with long-term value and environmental impact.
1. Long-Term Cost Analysis of Different Solutions
Evaluate stabilization methods through total cost of ownership:
| Solution Type | Initial Cost | Lifespan | Cost/Year | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone Pads | $25-$50 | 2-3 years | $10-$17 | Quarterly cleaning |
| Adjustable Straps | $35-$70 | 5+ years | $7-$14 | Annual tension checks |
| Platform Bed Frame | $200-$500 | 10+ years | $20-$50 | Biannual bolt tightening |
Hidden cost factor: Cheaper rubber pads often degrade faster in humid climates, requiring replacement every 12-18 months versus silicone’s 24-36 month lifespan.
2. Environmental Impact Considerations
Modern stabilization solutions vary significantly in sustainability:
- Natural fiber solutions (wool, hemp) offer biodegradability but typically last only 1-2 years
- Recycled rubber mats provide eco-friendly traction but may off-gas VOCs in warm environments
- Medical-grade silicone represents the most durable green option, with 300+ wash cycles before degradation
Emerging innovations include plant-based adhesives and mycelium (mushroom root) friction layers currently in development by sustainable bedding companies.
3. Future-Proofing Your Setup
Anticipate these coming trends when choosing solutions:
- Smart stabilization – Pressure-sensitive pads that adjust friction based on sleep position (prototypes show 40% better performance)
- Modular systems – Interchangeable components that adapt to mattress replacements or frame upgrades
- Nanotechnology coatings – Permanent microscopic texture treatments that won’t affect mattress feel
Professional recommendation: Invest in solutions with upgrade potential – like strap systems with standardized connectors or pads with replaceable friction layers.
4. Health and Safety Longevity Factors
Prioritize solutions that maintain safety over time:
- Avoid materials that become brittle (certain plastics) or overly sticky (some adhesives) with age
- Ensure washable components can withstand 60+°C water for allergen control
- Verify flame retardancy matches your mattress’s rating (especially important for memory foam)
Remember that proper stabilization should enhance your mattress’s lifespan by preventing edge wear and frame damage – factor this into your total cost calculations.
Specialized Solutions for Unique Sleeping Environments
Standard mattress stabilization methods often fail in unconventional sleeping setups. This section provides tailored approaches for challenging environments, drawing from marine, RV, and medical industry innovations adapted for home use.
1. Mobile Sleeping Solutions: RVs and Boats
Vehicle motion creates unique challenges requiring multi-point stabilization:
- Shock-absorbing underlayers – Use closed-cell foam pads (1/2″ thickness minimum) to dampen vibration while maintaining friction
- Perimeter lockdown system – Install marine-grade rail tracks with adjustable cleats every 12 inches for 360° security
- Dynamic tension straps – Elasticized corner straps with boat buckle adjusters accommodate movement without loosening
Technical insight: The ideal RV setup combines static friction (μs > 0.8) with 5-10% stretch capacity in retention systems to handle road vibrations.
2. Medical and Accessibility Considerations
For hospital beds or sleepers with mobility challenges:
- Low-friction tops/high-friction bottoms – Special dual-surface pads allow easy repositioning while preventing unwanted sliding (e.g., Sizewise Therapeutic Pad)
- Quick-release mechanisms – Medical-grade velcro (3″ width minimum) provides instant access in emergencies
- Washable barrier systems – Fluid-resistant friction layers that withstand daily sanitization (140°F+) without degradation
Safety protocol: Always maintain at least one completely non-slip surface (floor or bed) for transfer safety when using mobility aids.
3. Extreme Climate Adaptations
Temperature and humidity extremes affect material performance:
| Climate | Optimal Solution | Performance Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| High Humidity | Micro-perforated silicone | Maintains μ > 0.7 at 90% RH |
| Freezing Temps | Wool-felt hybrid pads | Functional to -20°F |
| Arid Conditions | Rubber-cork composite | Resists drying to 10% RH |
4. Integration with Smart Home Systems
Next-gen stabilization works with home automation:
- Pressure-sensitive alerts – Embedded sensors notify when mattress shifts >2° from baseline
- Auto-tensioning systems – Motorized straps adjust based on sleep position data
- Predictive adjustments – AI learns sleep patterns to preemptively increase friction during restless periods
Installation tip: When retrofitting smart components, ensure they don’t create new pressure points or interfere with mattress breathability.
Professional-Grade Mattress Stabilization Systems and Performance Validation
For those requiring industrial-strength solutions or seeking to validate their stabilization system’s effectiveness, this section details commercial-grade approaches and scientific testing methodologies used by sleep professionals.
1. Commercial Stabilization Systems Analysis
High-traffic environments (hotels, hospitals) use engineered solutions with measurable performance metrics:
| System Type | Shear Resistance | Compression Cycle Rating | Clinical Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Bed Lock | 150+ lbs lateral force | 50,000 cycles | ANSI/AAMI HE75 compliant |
| Hotel Retention System | 90 lbs lateral force | 25,000 cycles | ASTM F1566 certified |
| Therapeutic Positioning | 200+ lbs multi-directional | 100,000 cycles | FDA Class I medical device |
Key insight: These systems typically combine three friction layers with mechanical interlocks, achieving μ > 1.2 even when wet or under extreme temperatures.
2. DIY Performance Testing Protocol
Validate your home system’s effectiveness with these professional testing methods:
- Incline plane test – Gradually tilt bed to find slide initiation angle (15°+ indicates excellent stabilization)
- Shear force measurement – Use luggage scale to measure force required to move mattress (aim for >40 lbs resistance)
- Cyclic loading test – Perform 50 sit-to-stand transitions while measuring mattress displacement (<1″ total movement acceptable)
Advanced technique: Apply talcum powder between mattress and frame to visualize micro-movements during sleep using time-lapse photography.
3. Long-Term System Optimization
Maximize your stabilization system’s lifespan and performance:
- Material compatibility mapping – Create a cross-reference chart of all contact materials and their friction coefficients
- Wear pattern analysis – Use UV markers to identify high-stress areas needing reinforcement
- Seasonal adjustments – Increase strap tension by 10% in winter when materials contract
Professional maintenance schedule:
• Monthly: Inspect all contact surfaces
• Quarterly: Re-tension mechanical components
• Annually: Replace sacrificial friction layers
• Biannually: Full system validation testing
4. Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Address potential failure points through engineered safeguards:
- Secondary retention – Always install backup straps or pads rated for 50% of total load
- Emergency release – Ensure at least one stabilization method can be disengaged single-handedly
- Load monitoring – Use color-changing wear indicators on high-stress components
Remember: The most effective stabilization systems are invisible during use but immediately apparent when needed – this balance defines professional-grade performance.
Final Thoughts: Achieving Permanent Mattress Stability
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the science of mattress stabilization from basic friction principles to advanced commercial solutions. You’ve learned how to assess your specific sliding risks, implement targeted solutions (from silicone pads to strap systems), and even validate performance using professional testing methods.
Remember that effective stabilization combines proper material selection, strategic weight distribution, and regular maintenance – whether you’re dealing with a standard bed frame or specialized sleep environment.
Now armed with this knowledge, take action to transform your sleep experience. Start by implementing one primary solution from our recommendations, then layer additional methods as needed. Your perfectly stabilized mattress – and the uninterrupted sleep it enables – is just a few adjustments away. Sweet dreams!
Frequently Asked Questions About Preventing Mattress Sliding
What’s the most effective way to stop a memory foam mattress from sliding?
Memory foam’s lightweight construction requires a multi-pronged approach. Use a silicone-based non-slip pad (minimum 2mm thickness) combined with corner straps. The pad creates surface friction while straps handle lateral forces.
For adjustable bases, add a vertical retention bar at the headboard. This combination addresses memory foam’s unique properties – low density, smooth underside fabric, and temperature sensitivity that affects material grip.
How do I secure a mattress on a wooden platform bed without damaging it?
Opt for non-invasive solutions:
1) Felt furniture pads (1/4″ thick) placed every 12 inches along the frame edges
2) A breathable rug pad cut to size
3) Rubberized shelf liner between mattress and frame.
These create friction without adhesives. For extreme cases, use removable museum putty at contact points – it holds up to 5 lbs per square inch yet removes cleanly.
Why does my mattress still slide after using a non-slip pad?
Common causes include: incorrect pad size (should extend 2-3″ beyond mattress edges), dirty frame surface (clean with rubbing alcohol first), or insufficient weight distribution.
Heavy sleepers (>200 lbs) may need dual-layer pads or a pad combined with corner weights. Also check if your bed frame has any slight incline – even 2° of tilt can defeat friction solutions.
Are mattress straps safe for all bed types?
Straps work well for traditional frames but require caution with:
1) Adjustable bases (use only stretchable straps with quick-release buckles)
2) Floating beds (may compromise structural integrity)
3) Antique frames (can damage delicate wood).
Always check weight ratings – quality straps should withstand 50+ lbs of tension without stretching permanently.
What’s the difference between rubber and silicone anti-slip pads?
Rubber pads (60-70 durometer) offer immediate high friction but degrade faster (12-18 months). Silicone pads (80+ Shore A) maintain performance longer (2-3 years) and handle moisture better.
Silicone’s coefficient of friction remains stable (μ=0.6-1.0) across temperatures, while rubber becomes slippery when cold and sticky when hot. Medical-grade silicone is hypoallergenic – important for sensitive sleepers.
How can I stabilize a mattress for someone with mobility issues?
Use a dual-surface system: high-friction bottom (μ>0.8) against the frame with a low-friction top (μ<0.3) under sheets. This prevents sliding while allowing easy repositioning.
Install bed rails with quick-release mechanisms and consider pressure-activated friction pads that increase grip when occupied. Always maintain clear emergency access paths.
What’s the most cost-effective long-term solution?
A hybrid approach provides best value:
1) Inexpensive rug pad as base layer ($15-20)
2) Mid-range corner straps ($25-35)
3) DIY side rails from 1×4 lumber ($10).
This system lasts 5+ years with minimal maintenance. Compared to replacing slipped mattresses (which wear 40% faster), this $50-70 investment pays for itself in 18 months.
Can I make my own non-slip solution?
Effective DIY options include:
1) Marine-grade vinyl coated fabric (available at upholstery shops)
2) Recycled tire rubber mats (cut to size)
3) Layered shelf liner with spray adhesive.
For temporary fixes, use tennis balls sliced and placed under mattress corners. However, commercial solutions typically outperform DIY by 30-50% in friction tests and last 2-3x longer.